The screw cap refers to a closure mechanism where the cap is connected to the container through its own threaded structure and is secured by rotation.
Thanks to the advantages of the threaded structure, screw caps can generate significant axial force through the engagement of the threads when tightened, making it convenient to achieve self-locking functionality. Additionally, some precision-critical caps require threaded screw caps.
This article mainly introduces the mold design of plastic bottle caps with threaded structure.
Mold Release Methods
There are mainly three types of mold release methods for plastic bottle caps: forced demolding structure, rotary demolding structure, and shrink core structure.
a. Forced Demolding Structure:
When using a forced demolding structure, the shape of the threads must be restricted to be circular.
When forcibly ejecting the plastic parts, the parts should have sufficient elasticity during demolding (such as PE, PP, POM, etc.). Forced demolding should meet the following requirements: as shown in Figure (a), the part should satisfy (A-B)/B≤5%; as shown in Figure (b), the part should satisfy (A-B)/C≤5%. If the side shape of the part has irregularities and cannot be forcibly ejected, side core pulling structures should be used at this time.
b. Rotary Demolding Structure:
When using a rotary demolding structure, there are no significant restrictions on the selection of thread contours.
c. Shrink Core Structure:
When using a shrink core mold structure, there are no significant restrictions on the selection of thread contours. Usually, the threads are required to be intermittent rather than continuous in length.
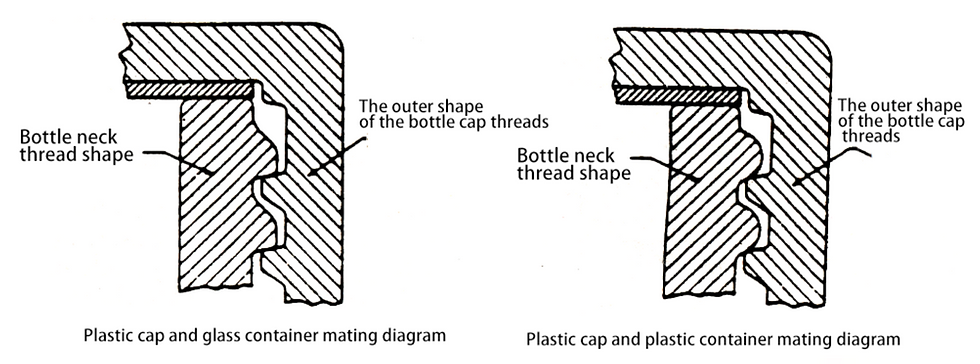
Introduction to Threaded Containers
In theory, to achieve the best sealing effect, the outer shape of the cap threads should be as close as possible to the gap between the two adjacent threads on the bottle neck, and both the cap and bottle neck should have a force angle in the horizontal direction.
In practice, achieving this optimal retention force is rarely possible due to the following reasons:
a. Caps and bottle necks are produced in multi-cavity molds, inevitably leading to differences between mold cavities.
b. Key dimensions of caps and bottle necks have acceptable tolerance ranges, such as T and E (maximum/minimum values of thread diameter), resulting in significant differences in thread fit under extreme conditions.
c. The materials of caps and bottles also affect the retention force due to differences in properties such as elasticity, hardness, strength, surface friction coefficient, and additives used in combination.
Designing Fit Dimensions
When determining various fit dimensions, the recommended standard size design from the following table can be referenced.
At De Varo Packaging, we are committed to providing innovative packaging solutions tailored to meet your specific needs. With our expertise and dedication to quality, we strive to exceed your expectations and become your trusted partner in packaging.






Comments